LiFePO4 batteries, also known as lithium iron phosphate batteries, are rechargeable batteries that use a cathode made of lithium iron phosphate and a lithium cobalt oxide anode.
They are commonly used in a variety of applications, including electric vehicles, solar systems, and portable electronics.

Safety Features of LiFePO4 Batteries
LiFePO4 batteries are known for their high level of safety compared to other lithium-ion battery chemistries. They have a lower risk of overheating and catching fire due to their more stable cathode material and lower operating temperature. We have also mentioned this in our best LiFePO4 battery list.
In addition, LiFePO4 batteries have a built-in protection circuit that prevents overcharge, over-discharge, and short-circuit. This is called a BMS.
Overcharge: If a LiFePO4 battery is charged beyond its maximum capacity (Ah), it can lead to overcharge. This can cause the battery to become unstable and potentially catch fire. This is why it is important to use a compatible charger and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for charging.
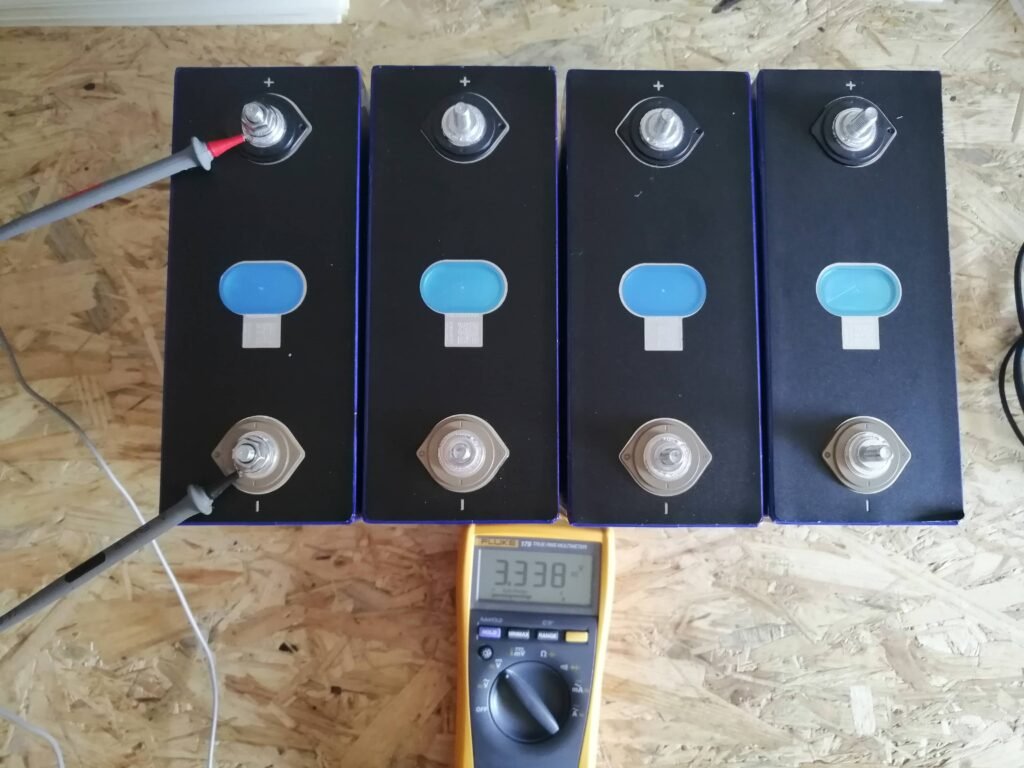
The image below shows the charging voltages of one cell, 12V, 24V, and a 48V battery. Avoiding the top 10% and the bottom 10% is better. To expand the battery’s lifespan, you should cycle the battery between 10 and 90%.
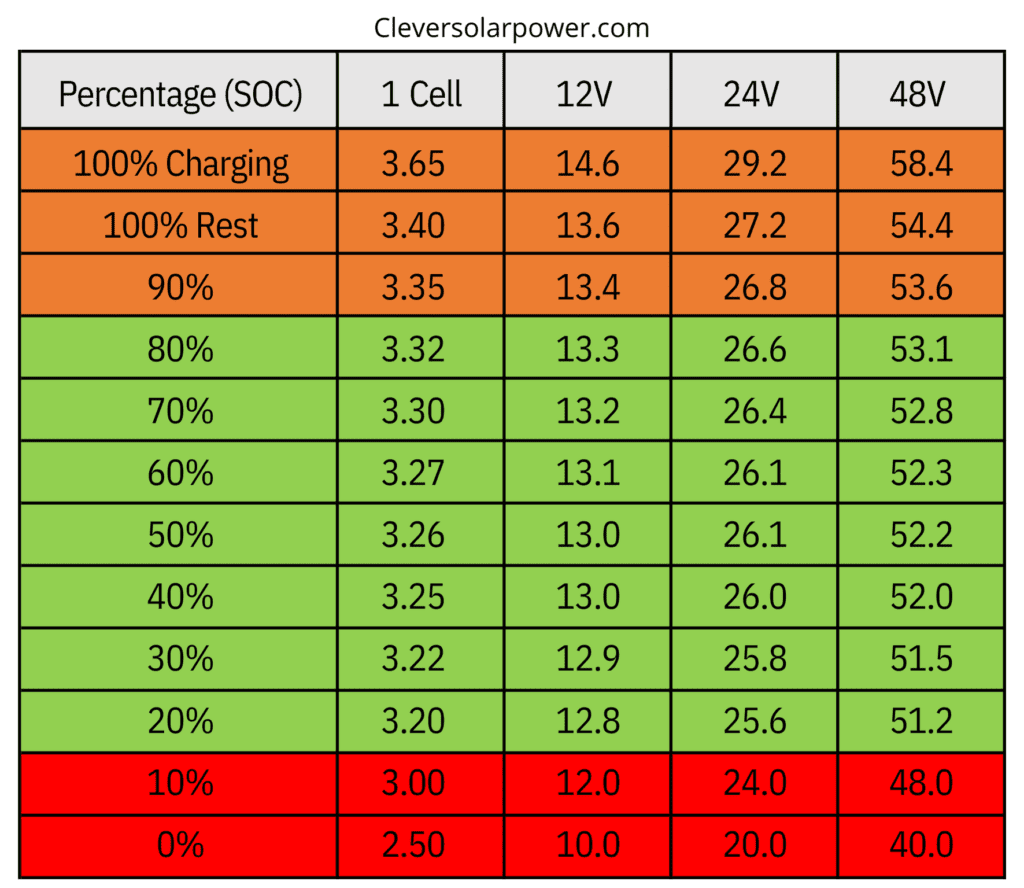
The charging current is usually at 0.5C. For example, a 100Ah lithium battery can be charged with 50Amps. I recommend using a simple 10A benchtop power supply to charge the cells for top balancing. After that, you can use a charger or inverter charger. I use a Victron multiplus 2 at home myself. This is an inverter charger.
Over-discharge: If a LiFePO4 battery is allowed to discharge too far, it can lead to over-discharge. This will damage the battery and reduce its overall lifespan. To prevent over-discharge, you should only discharge to 3V per cell or 12V.
Physical damage: This is especially true if you place the batteries in your vehicle. Strap them down or make a holder that keeps the battery in one place. If you work with raw lifepo4 cells, you need to have a divider in between the cells. Otherwise, the friction can rub away the blue plastic on every cell. If the blue plastic is rubbed off, the negative of one cell comes in contact with the other negative of another, which is not desirable.

High temperatures: LiFePO4 batteries can become unstable if exposed to high temperatures. The temperature of a battery increases if it is charged and discharged at high c-rates. It is important to store LiFePO4 batteries in a cool, dry place.
In general, it is recommended to store LiFePO4 batteries at a temperature between -20°C (-4°F) and 60°C (140°F). Some LiFePO4 batteries are designed to operate at higher temperatures, up to 75°C (167°F). This will depend on the specific battery and its design. Do not charge the battery when it’s at or below freezing. This will permanently damage the battery. Some batteries have internal heaters to operate in freezing temperatures.
Short-circuit: A short-circuit can occur if the positive and negative terminals of a LiFePO4 battery come into contact with each other. This can cause the battery to become unstable and potentially catch fire.
An improper education on how to wire batteries can create a short circuit. I had this myself when I wired up my first batteries in parallel. A faulty connection melted the battery stud and threw the bolt 20 feet away.
The second most occurring short circuit fault is dropping tools on the battery. Make sure to wrap electrical tape around your tools when working with batteries. Using safety glasses is also a good idea.
I have found a great study on short circuiting a LiFePO4 battery. Below are the excerpts. Here is the link to the full study.
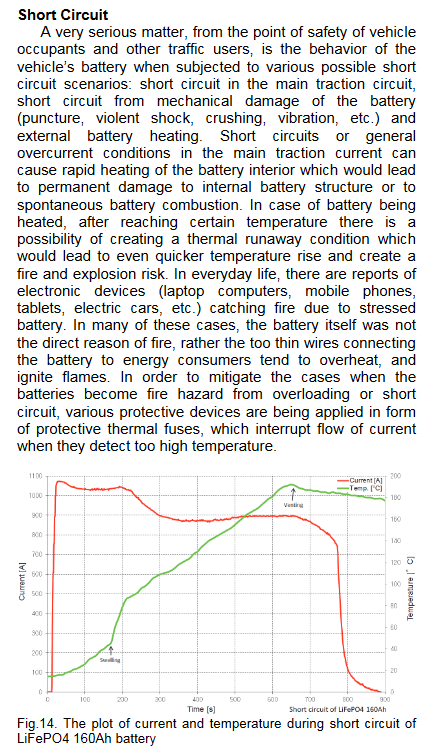



Potential Safety Risks of LiFePO4 Batteries
LiFePO4 batteries are generally considered to be safe. They do have some potential safety risks to be aware of. For example, they can still catch fire if damaged or subjected to extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or physical impact. It is important to handle LiFePO4 batteries with care and follow proper storage and usage guidelines to minimize the risk of accidents.
Handling and Maintenance of LiFePO4 Batteries
To ensure the safety of LiFePO4 batteries, it is important to handle and maintain them properly. This includes charging them using a compatible charger, storing them in a cool, dry place, and handling them gently to avoid damaging the battery.
Comparison to Other Battery Chemistries
Compared to other lithium-ion battery chemistries, such as lithium cobalt oxide and lithium manganese oxide, LiFePO4 batteries are generally considered safer. This is due to their more stable cathode material and lower operating temperature. They also have a lower risk of thermal runaway. This is a condition in which the battery’s temperature increases rapidly and can lead to a fire.
Other lithium-ion battery chemistries, such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) and lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4), have a high level of safety. Still, they have a higher risk of thermal runaway and overheating than LiFePO4 batteries. This is due to their higher operating temperature and less stable cathode material.
It is important to note that all types of lithium-ion batteries have some potential safety risks. It is important to handle and maintain them properly to minimize the risk of accidents and ensure their long-term performance. This includes using a compatible charger, following proper storage and usage guidelines, and handling the battery gently to avoid physical damage.
Watch this video about comparisons between LiFePO4, LTO, and Pouch cells (Li-pol):
Conclusion: Overall safety of LiFePO4 batteries
Overall, LiFePO4 batteries are considered to be a safe choice for a variety of applications due to their high level of stability and built-in protection features.
 I have written a book that contains all the information you need to get started with off-grid solar power.
I have written a book that contains all the information you need to get started with off-grid solar power.
With over 1,800 reviews at 4.5 stars, I can almost guarantee that this book will save you $100s on buying the right equipment.
You can get it here on Amazon.com

I’m an off-grid enthusiast. I created this website to give clear and straight-to-the-point advice about solar power. I’m also the author of the book ‘Off-grid solar power simplified‘. Read more about me on my about page, check out my Youtube channel, or send me a message.
Hello Nick,
Your above article is very informative and understandable for a non-electrical person.
As the LiFePO battery is safer than other lithium-ion battery chemistries, is it safe to carry in an airline cabin? I am looking to purchase a new Ecoflow portable power station with the LiFePO battery for camping.
Thank you.
Hello Kent,
I don’t think you can bring them on an airplane because they will see it as a lithium battery. They don’t know the difference between lithium batteries.
Sure you can: https://www.reddit.com/r/SolarDIY/comments/18drtkr/can_you_fly_with_lifepo4_batteries/
You won’t be able to get a large battery on board of a plane without approval first. You can try and let us know 😉
Thinking of putting 2 LFP 100AH batteries on my boat
once out at sea you don’t have anywhere to run
wondering if this is safe.
They are safer than lead-acid because every battery has a BMS.
while living in vehicle do have to worry about EMF’S/cancer with charger and fridge?
I don’t know much about EMF’s, but I didn’t hear bad things.