If you have an RV or an off-grid system and want to add a fridge, you will come across 12VDC and 120VAC fridges.
People are asking, which fridge should I go for? 12Volts DC or 120 Volts AC?
Let’s start with explaining the differences between 12VDC fridges and 120 or 230V AC fridges.
Differences between 12/24V DC and 120/230V AC fridges – 3 Types
We will first discuss the 12V DC fridges, then the 120/230VAC fridges. Lastly, the 12/24VDC compressor fridge.
12V DC Peltier fridge
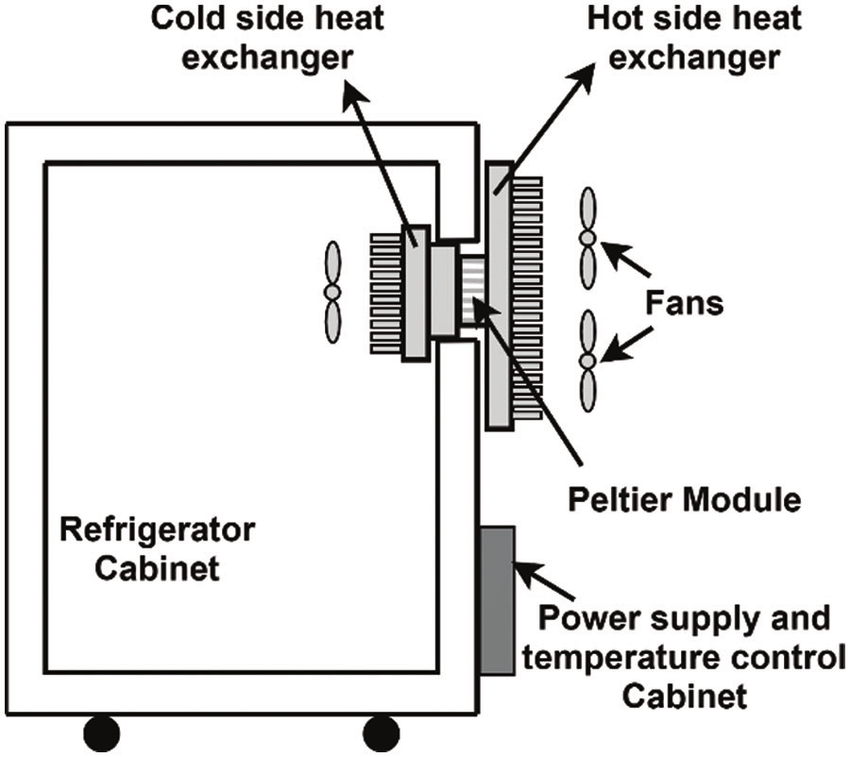
12V refrigerators, also known as thermoelectric coolers, work on the principle of the Peltier effect. In this system, when a DC electric current is passed through two different types of semiconductors, heat is transferred from one side of the device to the other, creating a cooling effect.
Advantages
- An inverter is not needed.
- No moving parts
- Silent operation
- Better withstanding vibrations because there are no moving parts
- Relatively cheap
Disadvantages
- Limited in size (usually very small)
- It cannot go as low in temperature as a compressor fridge (no freezing)
- Constant but high current draw compared to it’s cooling ability
If you look at the following image, you can see the fans inside and on the outside. This is to circulate the remove the hot air from the Peltier module. These kinds of fridges are not used much in a cabin or RV.

3-Way Absorption fridge
This is a fridge where you can use three ways of power. These are:
- Natural gas
- 12/24V DC
- 120/230V AC
These are the original camper fridges (absorption fridges). When your vehicle is on the road, you will use the 12V source, and when you are camping, you can use natural gas (propane) or shore power.
Advantages
- No moving parts (good for vibration while on the road)
Disadvantages
- Have to carry propane with you
- Propane detecting sensor is recommended
120/230V AC fridge
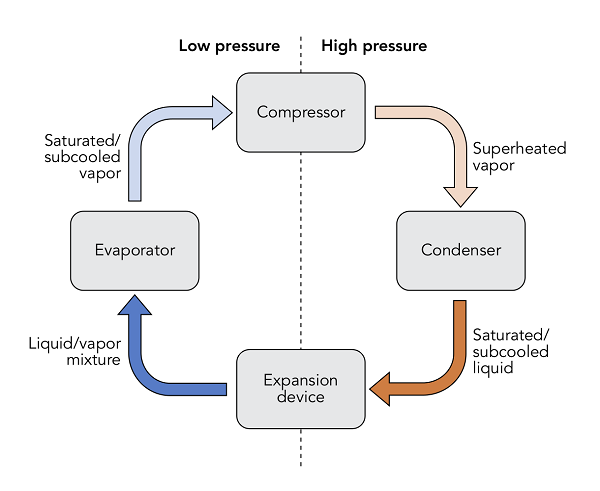
Most 120V or 230V AC fridges, typically found in homes, work on the principle of vapor-compression refrigeration. In this system, a liquid refrigerant evaporates in a low-pressure environment to absorb heat. Then it is compressed and condensed back into a liquid, releasing its heat to the outside. This cycle is repeated to cool the inside of the fridge continuously.
Advantages
- Efficient in cooling performance
- It can create very low temperatures
- Cheaper than Peltier coolers
- Large storage volume
Disadvantages
- You need an inverter to run these
Some examples are your typical mini, dorm, or tabletop fridge.

12V/24V DC compressor fridges
The last category is the 12/24 Volt DC compressor fridges.
A compressor fridge can only work with an AC signal, so an inverter inside the fridge converts the 12 or 24V to 120 or 230V AC.
Advantages
- It can work on 12 or 24V DC straight from the battery.
Disadvantages
- Expensive because of the built-in inverter
- You need thicker cables in order to wire the fridge due to the voltage drop
Comparison between 120V/230V AC and 12/24V DC fridges
In this section, I will talk more about the pricing of these two options.
Cost of 120/230V AC fridge
We will choose the RCA RFR322 Mini Refrigerator, which has 3.2 cubic feet of storage with a freezer compartment. An ideal size for a van or small cabin.
- Fridge cost: $157
- Inverter cost: $266
- total cost: $423
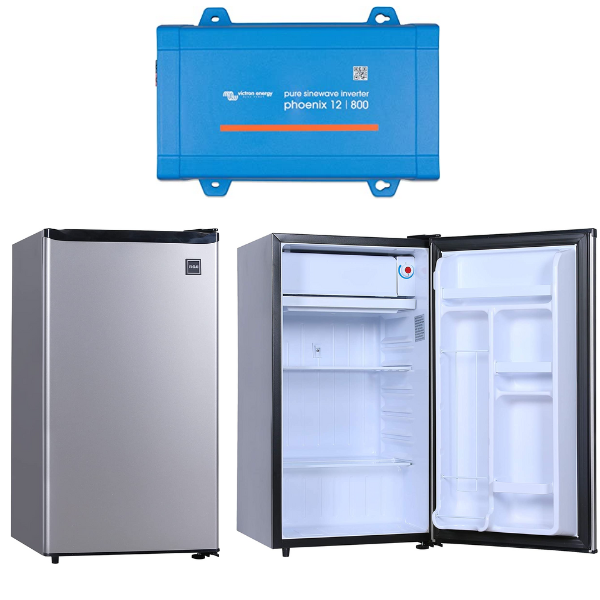

Cost of 12/24V DC fridge
We will choose the bestseller in this category, the BougeRV 12 Volt Refrigerator with 1 cubic foot of storage. This has no separate freezer compartment, but you can choose the whole compartment as a freezer or fridge.
- Fridge cost: $300

Conclusion
- We can see that the AC fridge costs more. But the DC fridge has only a third of the storage space of the AC fridge.
- The power consumption of the AC fridge will be a little more because of the idle draw of the inverter. However, this will be limited when you use the ECO mode on the Victron Phoenix inverter. Make sure you use an inverter with at least 6x the continuous power rating of the fridge. This is to handle the large startup power drawn from the compressor.
- You already have an inverter if you need to use other AC appliances.
- The ECO mode only works with older-style thermostat fridges, not newer electronically controlled ones. The ECO mode will turn the inverter off, even when the fridge’s electronic thermostat is working. So the compressor will never get a signal from the electronics to start. The ECO mode only works when the load is over 25 Watts.
My recommendation
If you need an inverter for other appliances, use an AC fridge and a pure sine wave inverter with an ECO mode. I recommend the Victron Phoenix line. The inverter will turn itself off when there is no load detected.
If you don’t need an inverter and can get used to using a smaller fridge, then a DC fridge is your best option.
Further reading: what size inverter do I need for an AC fridge?
[custom-related-posts title=”Related Posts” none_text=”None found” order_by=”title” order=”ASC”]
I’m an off-grid enthusiast. I created this website to give clear and straight-to-the-point advice about solar power. I’m also the author of the book ‘Off-grid solar power simplified‘. Read more about me on my about page, check out my Youtube channel, or send me a message.