Isolated and non-isolated DC-DC chargers are two types used to convert DC voltage from one level to another.
Their main difference is handling electrical isolation between the input and output circuits.
What is a Non-isolated DC to DC Charger?

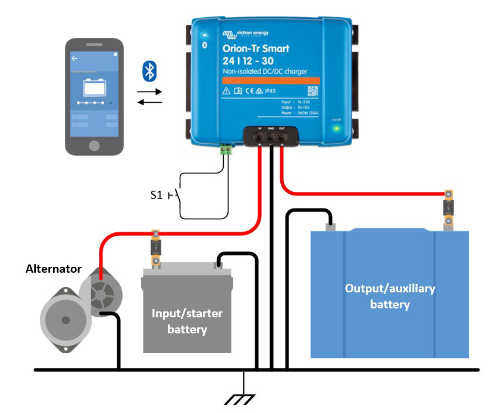
A non-isolated DC-DC charger, or a buck converter, works by using an inductor coil to regulate the output voltage.
This type of charger does not provide electrical isolation between the input and output circuits, and the input and output grounds are typically connected.
Non-isolated chargers are typically smaller, more efficient, and less expensive than their isolated counterparts. Still, they may not be suitable for applications that require electrical isolation or protection against voltage spikes.
What is an isolated DC to DC Charger?

In contrast, an isolated DC-DC charger, a boost converter or flyback converter, provides electrical isolation between the input and output circuits through a transformer or optocoupler.
This type of charger is typically larger, less efficient, and more expensive than non-isolated chargers, but it can provide essential benefits in specific applications. Isolated chargers can protect sensitive electronics from voltage spikes, isolate high-voltage or high-current circuits, and provide ground isolation for safety and noise reduction.

What is the Difference between isolated and non-isolated?
The main difference between isolated and non-isolated DC-DC chargers is the presence or absence of electrical isolation between the input and output circuits.
Non-isolated chargers are typically smaller, more efficient, and less expensive, while isolated chargers provide essential benefits regarding electrical isolation, noise reduction, and safety.
The choice between isolated and non-isolated chargers will depend on the specific requirements of the application and the level of electrical isolation and protection needed.
Efficiency
There are notable differences between an insulated and a non-insulated dc to dc charger regarding efficiency. We will compare the popular Victron Orion dc to dc chargers.
- Non-isolated: 95% efficiency
- Isolated: 87-89% efficiency
Price
We will compare two Victron TR smart dc to dc chargers:
- Victron Energy Orion-Tr Smart 12/12-30A Non-Isolated: $226
-
Victron Energy Orion-Tr Smart 12/12-30A Isolated: $270
Compatibility with alternator
The Victron Orion smart Isolated claims to be compatible with euro 5 and 6 engines (source). Read more about charging with an alternator here.
Common negative
The non-isolated dc to dc charger has a common negative. This means you need to use the negative busbar of your van or boat for the common negative. If this is not possible, use an isolated version with two inputs (+ and -) and two outputs (+ and -).
Which DC to DC charger do I need for charging a battery?
Consider an isolated converter for safety and noise reduction: If your system requires electrical isolation between the input and output circuits, or if you need to reduce noise or interference in your system, an isolated DC-DC converter may be the best option.
These converters use a transformer or optocoupler to provide electrical isolation between the input and output circuits, which can help prevent ground loops and reduce noise in your system.
My Recommendation
I recommend using a non-isolated version. This is mainly because of the price and the size.
If you use sensitive electronics like a radio, then get an isolated version.
[custom-related-posts title=”Related Posts” none_text=”None found” order_by=”title” order=”ASC”]
I’m an off-grid enthusiast. I created this website to give clear and straight-to-the-point advice about solar power. I’m also the author of the book ‘Off-grid solar power simplified‘. Read more about me on my about page, check out my Youtube channel, or send me a message.
Very informative. Explained in layman’s terms for a novice like me.
Thank you. it was extremely helpful, I needed the information, you have answered accurately